Difference between revisions of "Hooke's law"
(→Links) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Experiment Description= | =Experiment Description= | ||
| − | The purpose of this experiment is to verify the Hooke's law which relates the extension or compression of a spring with its exerted force given by | + | The purpose of this experiment is to verify the Hooke's law which relates the extension or compression of a spring with its exerted force given by <math> F = -k \times \Delta s </math>. |
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Who likes this idea= | =Who likes this idea= | ||
[[File:UAC.png|link=http://www.www.uac.pt/|border|179px|border|179px]] | [[File:UAC.png|link=http://www.www.uac.pt/|border|179px|border|179px]] | ||
| − | This experiment is currently hosted at University of | + | This experiment is currently hosted at University of Azores. The automation of the experiment was made by IST students as part of the e-lab project. |
| − | The first schools involved in hosting this distributed experiments were Escola Secundária Padre António Vieira, Alvalade/Lisboa and Externato Cooperativo da Benedita, Leiria. Escola Secundária Poeta Al Berto in Sines also | + | The first schools involved in hosting this distributed experiments were Escola Secundária Padre António Vieira, Alvalade/Lisboa and Externato Cooperativo da Benedita, Leiria. Escola Secundária Poeta Al Berto in Sines also cooperatein our project. |
=Experimental Apparatus= | =Experimental Apparatus= | ||
| Line 29: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:mola-montagem.jpg|thumb|alt=Experimental setup|Setup]] | [[File:mola-montagem.jpg|thumb|alt=Experimental setup|Setup]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The spring has 37.2 mm of which 10.0 mm are compressed windings (two sets of 14 windings). This means that the working length of the spring varies from 23.1 mm on compression to 32.4 on distension. | ||
It is possible to choose the compression/expansion limits of the spring and the velocity to detect possible hysteresis effects. | It is possible to choose the compression/expansion limits of the spring and the velocity to detect possible hysteresis effects. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
The user must specify the initial and final servo positions, the number of samples, the time interval between them and the number of cycles to execute (i.e. several compressions and/or distensions). This last option indirectly defines the speed at which the experiment occurs. | The user must specify the initial and final servo positions, the number of samples, the time interval between them and the number of cycles to execute (i.e. several compressions and/or distensions). This last option indirectly defines the speed at which the experiment occurs. | ||
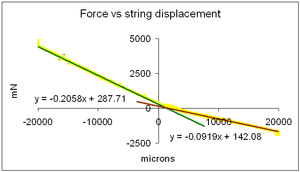
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:SpringForce.PNG|thumb|Adjusting two lines is needed to fit the hole experiment characteristic.]] |
=Links= | =Links= | ||
| − | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hooke | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hooke's_law wikipedia] |
*[[Lei de Hooke| Portuguese version (Versão em Português)]] | *[[Lei de Hooke| Portuguese version (Versão em Português)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 11 July 2015
Experiment Description
The purpose of this experiment is to verify the Hooke's law which relates the extension or compression of a spring with its exerted force given by [math] F = -k \times \Delta s [/math].
Links
- Video: rtsp://elabmc.ist.utl.pt/mola.sdp
- Laboratory: Basic in e-lab.ist.eu[1]
- Control room: Mola
- Grade: *
Who likes this idea
This experiment is currently hosted at University of Azores. The automation of the experiment was made by IST students as part of the e-lab project.
The first schools involved in hosting this distributed experiments were Escola Secundária Padre António Vieira, Alvalade/Lisboa and Externato Cooperativo da Benedita, Leiria. Escola Secundária Poeta Al Berto in Sines also cooperatein our project.
Experimental Apparatus
The apparatus is composed by a servo motor capable of compress or extend a spring by means of a rod. The spring distension is exactly measured by a potentiometer while the force is detected by a pressure gauge on top of the spring.
The spring has 37.2 mm of which 10.0 mm are compressed windings (two sets of 14 windings). This means that the working length of the spring varies from 23.1 mm on compression to 32.4 on distension.
It is possible to choose the compression/expansion limits of the spring and the velocity to detect possible hysteresis effects.
Protocol
The user must specify the initial and final servo positions, the number of samples, the time interval between them and the number of cycles to execute (i.e. several compressions and/or distensions). This last option indirectly defines the speed at which the experiment occurs.